Whitepaper
v1.0 – 2025-03-31

Executive Summary
LEA Blockchain is a next-generation decentralized infrastructure designed to bridge real-world asset (RWA) investment with the power of blockchain. By combining tokenized assets, transparent governance, and community-led project validation, LEA offers an inclusive ecosystem that democratizes access to opportunities previously reserved for institutional investors.
At its core, LEA enables users to stake LeaCoin ($LEA) to support and invest in real-world projects—such as real estate, renewable energy, and infrastructure—while earning potential returns. Every project must pass through a community-governed approval process, ensuring quality, trust, and alignment with ecosystem values.
Key Features
- Decentralized Governance: All project approvals and ecosystem changes are voted on by LeaCoin holders through a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization), empowering a truly community-led platform.
- Staking for RWA Access: Users can stake $LEA to participate in investment pools, provide liquidity, and gain exposure to income-generating assets.
- Validator Network: A trusted layer of validators conducts KYC, due diligence, and reputation staking to ensure only credible projects are presented to the DAO.
- Revenue-Backed Incentives: Approved projects share a portion of their earnings with stakers. Failed projects lead to locked tokens, creating a deflationary pressure that benefits the ecosystem.
Tokenomics Overview
LEA’s token economy is designed for long-term sustainability, market confidence, and active user participation. With a fixed total supply of 100 billion tokens, the distribution is as follows:
- 30% – Staking Rewards
- 20% – DAO Treasury
- 20% – Community & Ecosystem Growth
- 10% – Team & Founders (4-year vesting with 1-year cliff)
- 10% – Investors & Strategic Partners
- 5% – Liquidity Pools
- 5% – Reserve Fund
$LEA is used for governance, staking, transaction fees, validator deposits, and to gain access to investment opportunities within the platform.
Technological Foundation
LEA is built on Solana, a high-performance blockchain utilizing Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) for ultra-fast, low-cost, and energy-efficient operations. The platform uses WASM (WebAssembly) for cross-language smart contract development and is designed for cross-chain compatibility, allowing interaction with multiple blockchain networks.
Roadmap & Development Status
LEA is currently in its early-stage development phase, with key components of the platform architecture, tokenomics model, and governance mechanisms established. The Pre-Seed and Series A rounds are planned but not yet completed. Early supporters and strategic partners will play a crucial role in bringing the platform to life through these upcoming funding stages.
The roadmap includes:
- Initial MVP Launch with curated RWA project pools (e.g., tax-lien, solar energy)
- Gradual token release aligned with governance milestones
- Progressive decentralization through DAO governance expansion
- Expansion into new asset classes and global partnerships
Vision Forward
LEA envisions a future where real-world economic participation is no longer gated by intermediaries or high capital thresholds. Through tokenization, decentralized governance, and smart incentives, LEA empowers individuals and communities to invest, govern, and grow together.
By fusing blockchain innovation with tangible value creation, LEA is building the foundation for a fairer, more transparent financial ecosystem—accessible to all.
Introduction
Problem Statement
Traditional investment markets face significant inefficiencies that limit broad participation and fairness in wealth creation. High entry barriers often restrict access to promising opportunities, particularly for retail participants. Additionally, traditional financial markets frequently lack transparency, involve high costs due to intermediaries, and fail to adequately leverage technological innovations, perpetuating systemic inequities in global wealth distribution.
Proposed Solution
LEA addresses these challenges by providing a blockchain-based ecosystem designed to democratize access to real-world asset (RWA) projects. LEA’s decentralized platform eliminates intermediaries, lowers barriers to entry, and enhances transparency through blockchain technology and community-driven governance.
By enabling participants to stake their LeaCoins into various approved real-world asset project pools, LEA facilitates ecosystem participation, community engagement, and sustainable project development. LeaCoin holders actively decide which projects enter the ecosystem, ensuring alignment with community values and long-term sustainability.
Main Participant Groups
LEA Chain’s ecosystem consists of three main participant groups, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the seamless operation and growth of the platform:
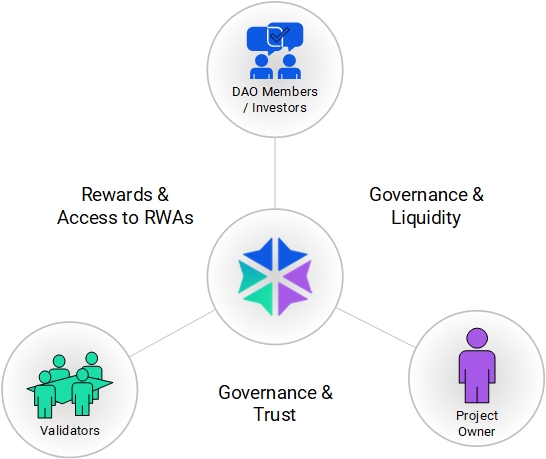
Project Owner
- These are the entities or individuals initiating real-world asset projects such as real estate developments, renewable energy ventures, and business fundings. They submit proposals to the LEA blockchain for evaluation and approval.
- Issues projects that are backed by Real-World Assets (RWAs).
- Provides rewards and access to RWAs to Validators and DAO Members / Investors.
Validators
- A specialized group responsible for conducting KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures, reputation staking, and due diligence on proposed projects. They ensure the credibility and feasibility of projects before they are presented to the DAO for voting.
- Conduct Governance & Trust processes through KYC and Due Diligence.
- Ensure the credibility of projects before they are presented to the DAO for approval.
- Earn rewards and access to RWAs in return for their validation work.
- Their role contributes to governance, ensuring the network’s credibility and sustainability.
DAO Members (LeaCoin Holders)
- The community of token holders who actively participate in governance decisions, staking, and liquidity provisioning. Through voting mechanisms, they decide which projects are accepted into the ecosystem and how resources are allocated.
- Provide Governance & Liquidity by staking LeaCoins and participating in governance decisions.
- Vote on projects proposed by Project Owners.
- Provide liquidity to the ecosystem through staking and investments.
- Receive rewards and access to RWAs as returns on their investments.
Key Objectives
- Lower Entry Barriers: Empower individuals to access high-value RWA projects through simplified processes enabled by community governance and LeaCoin staking mechanisms. By lowering capital requirements and enhancing access to traditionally exclusive opportunities, LEA democratizes RWA investments.
- Enhanced Transparency: Establish an immutable record of all transactions, governance decisions, and project milestones on the blockchain, providing a transparent and tamper-proof framework that enhances trust and accountability.
- Active Community Participation: Encourage active engagement from LeaCoin holders in project selection, governance proposals, and staking mechanisms. This inclusive approach fosters a vibrant and participatory ecosystem where decisions are made by the community for the community.
- Trust and Security: The validator group plays a crucial role in ensuring trust by performing thorough due diligence, reputation staking, and KYC validation before projects are approved. Their commitment and security deposits serve as a safeguard against malicious or low-quality projects.
- Sustainable Ecosystem Growth: Create a continuously evolving and resilient ecosystem through decentralized governance, ongoing liquidity provisioning, and adaptive staking mechanisms. This growth model ensures long-term value creation and ecosystem sustainability.
Through these core principles, LEA bridges blockchain innovation and real-world asset opportunities, creating a fair, accessible, and technologically advanced ecosystem that empowers participants to seamlessly invest in, manage, and benefit from tokenized real-world assets.
Rough Concept of Bridging RWAs with Blockchain Technology
The LEA blockchain platform bridges Real-World Assets (RWA) with blockchain technology through a seamless integration of decentralized governance, smart contracts, and real-world validation mechanisms. By combining the security, transparency, and efficiency of blockchain systems with tangible, off-chain assets, LEA offers a robust solution to modernize investment opportunities.
How It Works
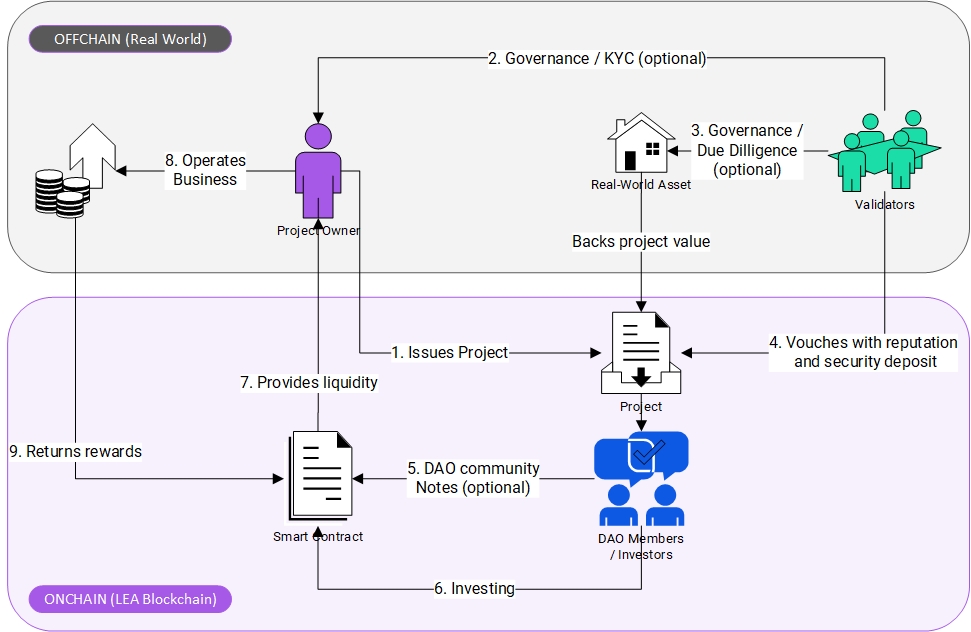
Project Issuance (Onboarding)
- Real-world asset projects, such as real estate, renewable energy, and infrastructure developments, are initiated by project owners. They propose their projects on the LEA blockchain for evaluation and acceptance.
- Fees: To access the project issuance features within the LEA Ecosystem, project owners must provide LeaCoins as fees for the project creation transaction process. Additionally, they need to pay a fee to incentivize validators to thoroughly validate the project owner’s identity and the project details.
Governance & Due Diligence (Validation)
- Validators perform KYC (Know Your Customer) and due diligence checks on proposed projects. They ensure the credibility of project owners and the feasibility of their projects (described in Governance and DAO Implementation).
- Validators are responsible only for verifying the legitimacy of the project owners and the correctness of their submitted documents. They are not liable for unforeseen consequences such as environmental disasters or external factors leading to project failure.
DAO Voting & Approval (Decentralized Decision-Making)
- The LEA DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) enables community-driven governance. DAO members (LeaCoin holders) vote on whether a project should be accepted into the LEA ecosystem. Approval requires reputation staking and a security deposit from validators, ensuring accountability.
Investment & Staking (On-Chain Commitment)
- Once approved, users can stake their LeaCoins to invest in projects. Smart contracts facilitate secure and transparent funding, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Project Operation (Off-Chain Management)
- Projects operate in the real world, backed by their underlying assets. These assets provide tangible value to the blockchain ecosystem.
Liquidity Provision (Ecosystem Growth)
- Investors can provide liquidity through staking and participation in various liquidity pools, enhancing the platform’s utility and scalability.
Revenue Sharing & Rewards (Economic Incentives)
- Revenue generated from successful RWA projects is distributed back to investors through smart contracts. Additionally, unsuccessful projects trigger the locking of staked LeaCoins, creating a deflationary effect and encouraging responsible participation.
Transparency & Accountability (Blockchain Integrity)
- All transactions, governance decisions, and project milestones are recorded immutably on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and building trust within the community.
This holistic approach establishes LEA as a decentralized, community-governed ecosystem that enables seamless integration of real-world assets with blockchain innovation. Through this model, LEA empowers participants to engage in diversified investment opportunities that were traditionally inaccessible or highly exclusive.
Market Opportunity
![Forecasted market size of real-world asset tokenization in several industries, including real estate, from 2023 to 2030 [1]](https://getlea.org/wp-content/uploads/market_opportunity.jpg)
The global tokenization market is projected to reach $10.9 trillion by 2030 [1], fueled by the increasing adoption of blockchain technologies and the demand for more accessible and diversified investment opportunities. As traditional investment barriers are dismantled through tokenization, assets like real estate, renewable energy projects, and infrastructure become more accessible to both retail participants and institutions. LEA positions itself as a pivotal participant in this transformative market. By targeting a diverse audience, including retail participants, asset managers, and institutional entities, LEA addresses the rising demand for decentralized platforms that connect real-world assets with blockchain technology. Research consistently highlights a surge in interest for tokenized platforms that deliver ecosystem participation opportunities and transparent governance mechanisms, which are central to LEA’s value proposition.
The platform’s initial focus on sectors such as real estate, renewable energy, and tax lien projects aligns with growing preferences for tangible, income-generating assets. This strategic alignment not only captures emerging market trends but also ensures scalable growth potential, positioning LEA to capitalize on an expanding global market while meeting evolving participant demands.
Platform Description
LEA is a decentralized blockchain platform specifically engineered to support Real-World Asset (RWA) projects through a secure, scalable, and efficient technological infrastructure. It provides an ecosystem in which businesses, developers, and participants can interact seamlessly through token staking, governance participation, and transparent project management.
LEA Coin
The LEA Coin serves as the foundational utility token within the entire LEA ecosystem, providing access to various functionalities and governance mechanisms. Key aspects of LEA Coin include:
- Transaction Fees: LEA Coins are required to pay transaction fees across the entire LEA ecosystem, ensuring network operation and security.
- Democracy Rights: Holding and staking LEA Coins grants users the ability to participate in governance processes, including voting on DAO decisions.
- Project Owner Usage: Project owners must utilize LEA Coins when creating new projects for fundraising, covering transaction fees, and providing incentives for validators to evaluate and validate projects.
- Governance Participation: Users can also utilize LEA Coins to become validators, providing security and reputation-based services within the ecosystem.
- Project Participation: Users can stake accepted cryptocurrencies into projects by paying transaction fees with LeaCoin, thereby enhancing project funding and liquidity.
Technical Infrastructure
Blockchain Architecture:
- LEA is built on a high-performance blockchain leveraging advanced smart contract technology. The underlying infrastructure ensures scalability, security, and high transaction throughput necessary for robust support of asset-intensive operations.
- The platform leverages technologies such as Rust-based smart contracts, Web3 interfaces, and a Solana-based blockchain architecture to achieve high transaction speeds, reduced costs, and enhanced security.
Smart Contracts and Token Staking
- LEA implements secure and audited smart contracts that govern staking, voting mechanisms, and project pool management.
- LeaCoin holders stake tokens to actively participate in various approved RWA pools, contributing to ecosystem liquidity and gaining governance rights.
Governance and DAO Implementation
DAO-Based Governance Model:
- LEA adopts a progressively decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) model to enable community-driven governance and transparent decision-making.
- Voting rights are granted to LeaCoin holders who actively participate in the ecosystem by staking their tokens.
- Voting power is determined by the LEA Coin stake height at the time of vote evaluation, which usually occurs within a pre-defined period (e.g., one week after the vote request).
- This approach ensures that decision-making power is distributed fairly among active participants and mitigates the risk of rapid vote manipulation.
Fraud Security Mechanisms:
- To maintain integrity within the LEA ecosystem, validators must provide security in at least one of two ways:
- Reputation-Based Security: Validators can establish credibility through verified identity processes (KYC) to ensure authenticity and accountability.
- Security Deposit Mechanism: Validators can provide a security deposit consisting of various assets such as cryptocurrencies, NFTs, or other approved tokens.
- Validators are only held accountable for their work and the promises they make. External factors such as environmental disasters or unforeseeable incidents that cause a project’s failure do not result in penalties against the validator.
- Punishments are strictly limited to cases of fraudulent activity, such as incorrect KYC or faulty due diligence.
- If a project owner fails to fulfill promises made to the DAO members, a Re-Validation Process is triggered. During this process:
- Independent validators are randomly selected to re-validate the claims made by the original validator.
- If the re-validation confirms the original validator’s assessment, the process concludes without consequences.
- If the re-validation reveals false information or misconduct, the validator’s security deposit and initial project fees are confiscated and redistributed to compensate the re-validators and affected investors.
Ecosystem Participation and Dynamic Value
- When LeaCoins are staked, they enter RWA pools, thus reducing token circulation.
- Revenue generated from real-world projects flows back into the LEA ecosystem, supporting ongoing platform enhancements and community initiatives.
- A dynamic economic mechanism ensures that even unsuccessful projects contribute to ecosystem sustainability through transparent governance and community oversight.
Community Notes Feature for LEA Blockchain
Introduction
The Community Notes feature is a new addition to the LEA Blockchain platform, aimed at enhancing communication and collaboration between investors and project owners. This feature ensures transparency, accountability, and information sharing throughout the lifecycle of Real-World Asset (RWA) projects.
Purpose
The purpose of Community Notes is to provide a decentralized, blockchain-integrated mechanism where investors and project owners can:
- Exchange project information and updates.
- Report and address fraudulent behavior or potential criminal activities.
- Collaboratively process issues that arise during project execution.
- Ensure transparency and revision control by storing notes immutably on the blockchain.
Key Functionalities
- Note Creation and Signing:
- Every participant who writes a Community Note must sign it with their wallet.
- Signing a note requires paying gas fees, ensuring only genuine participants contribute.
- Blockchain Storage:
- All Community Notes are stored on-chain, providing a permanent, transparent, and tamper-proof record of communication.
- Notes are associated with specific projects, making it easy to track discussions relevant to each RWA.
- Revision Control:
- Once submitted, a Community Note cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring accountability.
- Additional notes can be appended to previous entries to provide updates or corrections.
- Accessibility:
- Community Notes are viewable by all participants involved in a particular project.
- Project Owners, Validators, and Investors can access and review notes to maintain clarity and transparency.
- Fraud Reporting Mechanism:
- In the event of suspicious activity, users can submit notes indicating potential fraudulent behavior.
- These reports are escalated to Validators for review and possible re-validation processes.
- User Verification:
- Notes are verified by their associated wallet signatures to ensure authenticity.
Benefits
- Promotes transparency and accountability within the ecosystem.
- Facilitates communication between stakeholders, enhancing project management and collaboration.
- Provides a mechanism for reporting fraudulent or suspicious behavior in a decentralized manner.
Future Enhancements
- Integration of a reputation system to highlight trustworthy participants.
- Implementing notification mechanisms to alert relevant parties about new Community Notes related to their projects.
This feature aligns with LEA’s vision of fostering a transparent and community-governed ecosystem by enabling open communication between stakeholders while ensuring accountability through blockchain technology.
Cross-Chain Compatibility
The LEA Blockchain is designed with interoperability at its core, enabling seamless integration with multiple blockchain ecosystems. This cross-chain compatibility is essential for enhancing liquidity, expanding asset utility, and providing users with a flexible and adaptable investment experience.
Key Features of Cross-Chain Compatibility
- Interoperability Protocols: LEA implements cutting-edge interoperability protocols that allow the seamless transfer of assets and data between various blockchain networks. The platform utilizes Wormhole as its primary cross-chain bridge, enabling secure and efficient transfer of assets across supported networks. Wormhole’s robust infrastructure provides the reliability and scalability needed for LEA’s multi-chain ecosystem.
- Enhanced Liquidity: Cross-chain compatibility allows assets on the LEA Blockchain to be utilized within broader blockchain ecosystems, increasing overall liquidity and usability. This feature enables investors to tap into various decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enhancing their staking and investment opportunities.
- Broadening Asset Utility: Projects utilizing the LEA Blockchain are not limited to the LEA ecosystem alone. Instead, they can interact with other blockchain networks, enhancing their utility and appeal to a wider range of participants. This is particularly important for Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization, where interoperability provides greater accessibility and investment potential.
- Security and Trust: To maintain robust security while facilitating cross-chain interactions, LEA employs cryptographic proofs and secure smart contracts. Wormhole’s bridging technology further ensures that transactions remain tamper-proof and transparent, even when assets are bridged across different networks.
- Scalability: By enabling interactions with other blockchain systems, LEA effectively distributes transactional loads across multiple networks. This enhances the scalability of the platform, making it more resilient to congestion and high traffic periods.
- DAO Integration: The LEA DAO governance model supports cross-chain compatibility by enabling community members to vote on interoperability proposals. This approach ensures that the development of cross-chain features aligns with community preferences and ecosystem growth strategies.
The inclusion of cross-chain compatibility strengthened by Wormhole bridging technology ensures LEA’s mission of bridging Real-World Assets (RWA) with blockchain technology. By enhancing connectivity with other ecosystems, LEA ensures greater liquidity, accessibility, and utility for its participants.
DAO and Transparency
- LEA is progressively adopting a semi to fully decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) model, ensuring transparency and increased governance participation.
- All transactions, governance decisions, and staking actions are transparently recorded and immutably stored on the blockchain, reinforcing participant trust and ecosystem integrity.
Tokenomics
LEA’s tokenomics model is designed to promote long-term sustainability, community engagement, and robust market dynamics. With a fixed total supply of 100 billion tokens, the distribution strategy ensures balanced incentives for participants and strategic partners, as well as ecosystem growth and stability.
Total Supply and Distribution
- Total Supply: 100,000,000,000 tokens
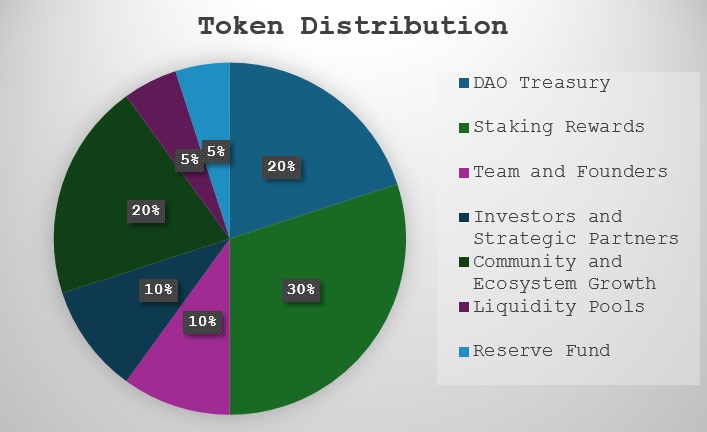
The distribution is structured as follows:
| Category | Percentage | Tokens | Description |
| DAO Treasury | 20% | 20,000,000,000 | Funding DAO operations, community incentives, ecosystem growth, and RWA project investments. Gradually unlocked based on DAO governance and funding milestones. |
| Staking Rewards | 30% | 30,000,000,000 | Incentivizing staking and active participation. Gradually distributed based on staking participation. |
| Team and Founders | 10% | 10,000,000,000 | Allocated to team and advisors with a structured 4-year vesting period and 1-year cliff. |
| Investors and Strategic Partners | 10% | 10,000,000,000 | Supporting early-stage and strategic investors, |
| Community and Ecosystem Growth | 20% | 20,000,000,000 | Used for community incentives, airdrops, governance participation, and ecosystem adoption. Gradual unlock based on achieved milestones. |
| Liquidity Pools | 5% | 5,000,000,000 | Ensuring market liquidity, gradually unlocked based on market needs. |
| Reserve Fund | 5% | 5,000,000,000 | Reserved for operational expenses, unforeseen events, and special community rewards. Released gradually based on project needs. |
Strategic Objectives of Tokenomics
Preventing Inflation:
- Fixed Total Supply: Capped at 100 billion tokens with no future minting, ensuring token scarcity.
- Gradual Token Distribution: Tokens, particularly for staking rewards and the DAO treasury, are unlocked progressively to prevent market oversupply and price volatility.
Avoiding Pump-and-Dump Schemes
- Controlled Liquidity: Allocation to liquidity pools to maintain market stability.
- Structured Vesting: Strict vesting schedules for team, founders, and early investors to align incentives with long-term project success and deter rapid token sell-offs.
- Incentivized Long-term Participation: Reward mechanisms tied explicitly to sustained project engagement and active ecosystem contribution.
Clear Utilization of Tokens
- Governance: Empower token holders to participate actively in decision-making and governance within the DAO.
- RWA Project Participation: Tokens fund real-world asset projects, offering holders direct involvement in tangible asset investments.
- Transaction Fees: Ensure consistent demand for tokens through their mandatory use for transaction fees across the LEA network.
- Buyback and Burn Strategy: Implement mechanisms for token buybacks and burning to control supply, enhancing token value sustainably.
Through these strategic decisions, LEA’s tokenomics ensures sustainability, robust engagement, and the successful realization of its ecosystem objectives.
Token Sale and Investment Rounds
Tokens allocated for Investors and Strategic Partners are distributed across structured funding rounds:
Pre-seed Rounds:
- Batch 1: 1.5B token at 0.0001$ per $LEA
- Batch 2: 2B token at 0.0003$ per $LEA
- Batch 3: 2B token at 0.0005$ per $LEA
- Batch 4: 500M token at 0.0008$ per $LEA
Series A:
- 4B token at 0.001$ per $LEA
These rounds target early supporters, strategic investors, and institutional investors who align with the long-term vision of LEA.
Vesting Schedules
To ensure long-term alignment and mitigate volatility:
Team and Founders:
- 4-year vesting with a 1-year cliff (25% unlocked after year 1, then incremental unlocks annually).
Community and Ecosystem:
- Gradual unlock based on project and community milestones over 4 years.
Staking Rewards:
- Gradually distributed as staking rewards earned by participants.
Technical Architecture
The Technical Architecture of LEA forms the backbone of its decentralized ecosystem, delivering scalability, security, and seamless integration for real-world asset (RWA) tokenization. As a Layer 1 blockchain solution, LEA is designed from the ground up to support high-performance decentralized applications (dApps) and tokenized assets without relying on external scaling layers.
LEA employs a high-throughput consensus mechanism, ensuring efficient transaction processing and network stability. Its smart contract framework is built to facilitate secure and automated interactions, supporting staking, governance, and RWA management. By implementing advanced cryptographic security measures and a decentralized network architecture, LEA ensures resilience against attacks and maintains full transparency in governance.
Designed for cross-chain compatibility, LEA enables seamless interoperability with other blockchain networks, expanding liquidity and asset usability. This chapter explores the core components of LEA’s technical architecture, including security protocols, smart contract functionalities, consensus mechanisms, and asset token integration, demonstrating how its Layer 1 infrastructure is optimized for decentralized finance and next-generation asset tokenization.
Technology Basis: Solana Blockchain
Solana is a high-performance, decentralized blockchain platform known for its speed, scalability, and low transaction costs. Created by Anatoly Yakovenko in 2017, Solana uses a unique combination of Proof of Stake (PoS) and a novel consensus algorithm called Proof of History (PoH) to handle thousands of transactions per second efficiently.
Why Solana?
- Solana processes transactions in parallel, using its Sealevel runtime.
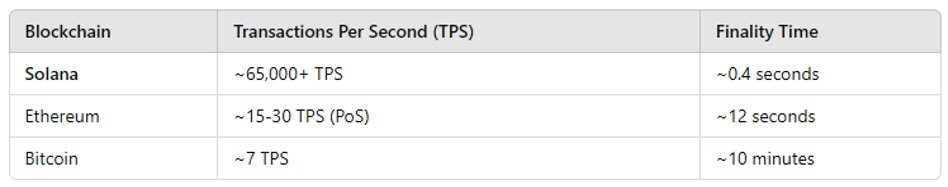
- Solana fees are a fraction of a cent, making it ideal for microtransactions, DeFi, and NFTs.
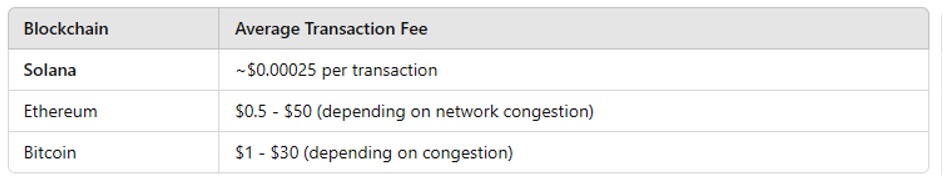
- Solana scales natively without relying on Layer 2 solutions like Ethereum (Polygon, Arbitrum).
- Solana’s Proof of Stake (PoS) is extremely energy-efficient.
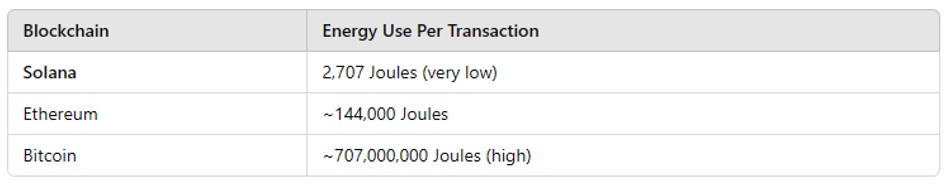
- Solana allows parallel execution of smart contracts (Ethereum processes one at a time).
WASM Engine instead of eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter)
A WebAssembly (Wasm) engine is used for executing WebAssembly bytecode, a low-level binary instruction format designed as a portable compilation target for programming languages. It enables high-performance applications to run efficiently inside browsers, servers, or embedded environments.
Use Case: Smart Contracts
Why WASM Engine?
- Broader Adoption & Ecosystem Support
- WASM is widely adopted in web technologies, blockchain networks (Polkadot, Ethereum via Ewasm), and cloud computing.
- Large community support leads to better tooling, documentation, and compatibility with various platforms.
- Multi-Language Support
- WASM supports many languages (Rust, C, C++, Go, AssemblyScript, etc.), making it easier for developers from different backgrounds to write smart contracts.
- eBPF primarily supports C and Rust, limiting developer flexibility.
- Standardized Execution Environment
- WASM is a widely accepted standard backed by the W3C, ensuring long-term stability and compatibility across platforms.
- eBPF is optimized for Linux kernel operations, making it less suited for cross-platform smart contract execution.
- Better Developer Experience
- Existing WASM tooling (such as WebAssembly runtimes, debuggers, and compil ers) makes development, testing, and debugging easier.
- More IDE and framework support compared to eBPF, which has a steeper learning curve and limited tooling.
- Security and Isolation
- WASM offers built-in sandboxing, preventing malicious code from affecting the system.
- eBPF has a more complex security model, designed for kernel operations, requiring stricter validation.
- Cross-Platform Execution
- WASM runs on browsers, cloud, and blockchains, making it a truly portable execution environment.
- eBPF is designed for Linux environments, making portability to non-Linux platforms more difficult.
- Scalability and Performance
- WASM is optimized for lightweight, efficient execution across different environments.
- eBPF is optimized for kernel-level performance, which may not be necessary for smart contract execution.
Transaction Ordering/Execution Mechanism: Proof of History (PoH)
LEA leverages Proof of History (PoH) to establish a verifiable and tamper-proof ordering of transactions before they reach consensus. The selected leader (validator) timestamps transactions using a cryptographic clock, creating a sequential, immutable record of events. This allows validators to independently verify timestamps without continuous network-wide communication, significantly reducing latency and computational overhead.
The Result?
- Faster Transaction Finalization – Transactions are processed in an optimized sequence, minimizing delays.
- Higher Throughput – Capable of handling 65,000+ transactions per second (TPS).
Why PoH?
Unlike traditional consensus mechanisms that require validators to constantly communicate about transaction order, PoH pre-orders transactions cryptographically, allowing the network to process blocks more efficiently. This innovation enhances speed, scalability, and overall network performance, making LEA an ideal foundation for high-demand decentralized applications (dApps) and real-world asset tokenization.
Consense Mechanism: Proof of History (PoH)
Validators stake tokens to secure the network and participate in block production. The more tokens staked, the higher the probability of being selected as a leader (block producer), ensuring an equitable and incentivized consensus process.
This staking mechanism serves as a defense against Sybil attacks, preventing malicious actors from overwhelming the network with fake identities. By requiring a financial commitment, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) enhances both decentralization and economic security, ensuring the integrity and stability of the blockchain.
Why PoS?
PoS is a more efficient and eco-friendly alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW), eliminating the need for energy-intensive mining. It enables high-speed transaction processing, lower operational costs, and a sustainable blockchain infrastructure, making it ideal for scalable decentralized ecosystems.
Roadmap
The LEA platform is strategically designed to advance asset tokenization and decentralized finance through clearly defined phases, aligning with our robust tokenomics model and vesting schedules. The roadmap for LEA’s evolution is outlined below:
- Concept Development & Pre-seed Phase (Months 1–6)
- Refinement of the LEA platform vision and establishment of strategic frameworks.
- Assembly of an expert core team in blockchain technology and asset management.Initiation of comprehensive regulatory compliance protocols.
- Execution of Pre-seed funding round, allocating 6,000,000,000 tokens to early supporters across multiple batches, ensuring foundational capital and community engagement.
- Seed & Infrastructure Development (Months 6–12)
- Implementation of the core smart contract infrastructure.
- Strengthening strategic partnerships with initial asset managers, laying groundwork for Asset Staking Pools & Projects.Launch of beta testing for the USDC claim interface, emphasizing transparency and efficiency in payouts.
- Continuation of funding efforts with clear alignment to token distribution, ensuring stability and strategic partner integration.
- MVP Platform Launch (Month 13)
- Series A & Platform Readiness (Months 14–18)
- Conduct Series A funding round, allocating 4,000,000,000 tokens to scale development and onboard venture capital and strategic institutional investors.
- Finalizing platform development with robust testing and security audits to ensure readiness for public launch.
- Initiating marketing campaigns targeting institutional investors and early community adopters to solidify market presence.
- Official Platform Launch (Month 18)
- Public launch of the LEA platform featuring the inaugural release of Asset Staking Pools & Projects,
- Activation of the USDC claim interface enabling LeaCoin holders to generate passive returns.
- Expansion of operational capabilities to effectively manage initial investor influx and ecosystem interactions.
- Sustainable Expansion & Ecosystem Growth (Month 19+)
- Gradual introduction of diversified Asset Tokens, expanding into asset classes such as container ships and aircraft leasing to broaden market opportunities.
- Progressive unlocking of tokens for staking rewards, community, ecosystem growth, liquidity pools, and DAO treasury as per strategic vesting schedules.Continuous global partnership development, driving adoption through collaborative ventures.Deployment of advanced analytics tools, portfolio management features, and UX/UI enhancements to meet evolving investor demands.
- Ongoing community governance to inform strategic decisions, ensuring long-term sustainability and responsiveness to market dynamics.
This roadmap demonstrates LEA’s commitment to leveraging structured tokenomics, disciplined token distribution, and strategic vesting schedules to foster growth, stability, and sustained value creation in decentralized finance and asset tokenization.
Team
LEA’s core team is comprised of dedicated and skilled professionals specializing in blockchain technology, business informatics, and platform management. Although currently compact, our team has been strategically selected to address all critical aspects of LEA’s successful development, from infrastructure design to strategic business integration.
Core Team Members
- Allwin Ketnawang – Blockchain Expert
Allwin is an experienced specialist in blockchain development and smart contract engineering, pivotal for developing and optimizing the LEA infrastructure. He brings expertise in robust security, seamless scalability, and exceptional user experience. His professional background also includes extensive experience in blockchain security audits, having successfully led numerous high-stakes penetration tests. Allwin has over 10 years of experience in blockchain solutions and has conducted extensive penetration testing and security analyses, further solidifying his capability to safeguard LEA’s technological infrastructure. - Andre Hassan – Business Informatics, M.Sc.
Andre combines extensive knowledge in business informatics with a proven ability to bridge technology and business operations effectively. His role focuses on managing and optimizing processes essential for executing large-scale IT solutions and ensuring operational excellence within the LEA platform. Andre has also successfully led a software quality assurance company, further demonstrating his capability in delivering high-quality, reliable software services.
Together, Allwin and Andre form the cornerstone of LEA, leveraging their combined expertise to deliver a secure, scalable, and user-centric blockchain ecosystem poised for continuous growth and innovation.
Strategic Advisors and Partners
We are actively seeking additional strategic advisors and planners with expertise in regulatory compliance, institutional investment, asset management, and other key areas. The involvement of new advisors will further empower LEA to identify high-value investment opportunities and expand its reach into untapped markets.
Development Milestones
From its inception during the Concept Development phase, the team prioritized regulatory compliance and assembled this multidisciplinary group of experts. As outlined in the roadmap:
- During the Pre-Seed Phase, core team formation was a foundational milestone.
- Throughout subsequent funding phases, the team continued to grow, aligning its expertise with the platform’s expanding needs.
This collective strength ensures that LEA remains at the forefront of decentralized finance, delivering a secure, efficient, and user-centric platform for asset tokenization.
Regulatory Compliance
LEA prioritizes regulatory compliance, aligning closely with international legal standards to cultivate trust among investors, partners, and the community. The platform’s comprehensive compliance strategy includes:
- Jurisdictional Adherence: LEA operates strictly within legal frameworks of approved jurisdictions. Compliance processes were proactively initiated during the project’s development phase, laying a solid foundation for lawful operations.
- Transparent Governance: Utilizing blockchain-based smart contracts and decentralized governance mechanisms, LEA ensures transparency and accountability across token distributions, funding activities, and ecosystem developments, maintaining compliance with applicable regulations.
- Investor Protection: LEA integrates best practices in governance to safeguard investor interests, incorporating democratic processes and transparent decision-making. This ensures that community-driven assessments guide the approval of new projects, promoting security and accountability.
- Dynamic Regulatory Updates: LEA is committed to continuously evolving its compliance strategies, adapting and integrating additional regulatory standards as the project progresses and expands into new asset classes and markets.
By embedding compliance within its core operational processes, LEA assures legality, strengthens investor confidence, and fosters sustainable ecosystem growth.
Risk Factors
Market Volatility
Blockchain and cryptocurrency markets are inherently volatile due to fluctuating economic conditions, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts. However, unlike many other blockchain projects, the value of LeaCoins is partially backed by real-world asset projects (RWA), such as Tax-Lien and Solar projects. This backing provides a fundamental value that may reduce the extreme volatility commonly associated with speculative blockchain projects lacking tangible asset support.
While this structure offers some degree of stability, market volatility can still significantly impact token valuations and investor sentiment.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Diversifying revenue streams through tokens backed by real-world assets to further enhance stability and minimize dependence on purely speculative market activities.
- Maintaining transparent and proactive communication with stakeholders to reinforce trust and stability during market turbulence.
- Continuously evaluating and adjusting staking and governance mechanisms to ensure alignment with long-term value creation and ecosystem growth.
Regulatory Changes
The dynamic regulatory environment presents potential risks including increased compliance demands or even the possibility of restrictive bans in certain regions.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Adopting proactive compliance frameworks during initial project development to ensure global and local regulatory alignment.
- Continuous legislative monitoring, enabling agile adjustments to the platform’s operational and compliance strategies.
Technological Risks
Blockchain technology, while innovative, introduces vulnerabilities such as potential cyber-attacks, smart contract flaws, and the risk of technological obsolescence.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implementing comprehensive security protocols, including regular third-party audits and rigorous smart contract testing.
- Establishing a dedicated technical team responsible for ongoing infrastructure maintenance, upgrades, and the implementation of innovative technological improvements.
- Ensuring compatibility with various blockchain ecosystems to enhance liquidity and broaden platform utility.
Liquidity Risks
Low token liquidity or inadequate liquidity in underlying assets can negatively affect token usability and valuation. Furthermore, gradual token unlock schedules may lead to sudden market disruptions if large stakeholders sell substantial portions of their holdings.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Developing strategic partnerships with leading asset managers and financial institutions to enhance liquidity.
- Controlled, periodic token releases from the foundation’s allocation, governed by community protocols, to maintain market equilibrium.
- Structuring vesting schedules for team members, investors, and strategic partners to prevent sudden sell-offs.
Operational Risks
Project execution can be hampered by operational delays, resource mismanagement, or unforeseen developmental obstacles, potentially disrupting critical milestones.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Clearly defined project roadmaps with milestone-based tracking and regular stakeholder updates.
- Allocating sufficient resources to operational management and ecosystem development, ensuring resilience and the ability to achieve strategic objectives.
Tokenomics-Related Risks
The structured distribution and unlocking of tokens, especially those reserved for staking, DAO Treasury, and liquidity pools, present risks of market oversupply and price instability. Additionally, discrepancies between early investors who acquired tokens at significantly lower prices and new entrants may create valuation disparities.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Gradual and transparent token unlock schedules to prevent sudden market flooding and speculative volatility.
- Ensuring alignment of stakeholder incentives through vesting mechanisms and community governance protocols.
- Implementing buyback and burn strategies to regulate token supply and enhance market stability.
Project Execution Risks (RWA Projects)
The integration of real-world asset projects presents unique challenges, including project failure, underperformance, or unforeseen market conditions that may affect returns. The initial vetting of these projects is conducted by validators through rigorous KYC processes and comprehensive due diligence to ensure legitimacy and viability. However, the final selection and acceptance of new projects are performed through crowd intelligence by all DAO members via decentralized governance mechanisms.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Careful selection and vetting of RWA projects through thorough KYC processes and due diligence conducted by validators.
- Empowering the community of DAO members to participate in decision-making, ensuring collective wisdom is applied in project approval.
- Re-validation processes to ensure accountability when projects underperform or deviate from their original commitments.
- Transparent governance mechanisms to ensure that project failures are properly addressed and compensated when applicable.
Governance and DAO-Related Risks
The LEA ecosystem’s governance model relies on community-driven decision-making, which may be vulnerable to voting manipulation, governance attacks, or centralization if a small group of stakeholders accumulates excessive voting power.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implementing reputation staking and security deposits to ensure validators act responsibly.
- Enhancing voting mechanisms to prevent governance attacks and encourage decentralized decision-making.
- Regularly updating governance protocols to adapt to changing ecosystem dynamics.
By systematically addressing these risks through targeted mitigation actions, LEA strengthens its ability to achieve stability, build investor confidence, and drive sustained ecosystem growth.
Conclusion
LEA embodies the future of decentralized finance and asset tokenization, connecting blockchain innovation with tangible, real-world investment opportunities. Through a meticulously designed tokenomics structure, LEA ensures sustainable growth, active community engagement, and market stability. With a capped total supply of 100 billion tokens, LEA strategically mitigates inflationary pressures and market volatility, fostering a secure and transparent economic environment.
The project’s comprehensive vesting schedules for team members, founders, investors, and strategic partners align stakeholder incentives with the long-term health and stability of the ecosystem. By allocating substantial tokens to DAO treasury, staking rewards, and community-driven growth initiatives, LEA actively empowers community participation and governance, driving collective decision-making and enhanced ecosystem integrity.
Our structured funding rounds—successfully completed through targeted Pre-seed and Series A investments—highlight strong investor confidence and commitment to LEA’s mission. The phased release and progressive unlocking of tokens further ensure market equilibrium and discourage speculative volatility, safeguarding long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
Looking forward, LEA will continually expand its ecosystem through innovative partnerships, diversification into new asset classes such as renewable energy, real estate, and infrastructure projects, and consistent upgrades to its technical infrastructure. Our commitment to regulatory compliance, robust security measures, and transparency ensures a trusted and reliable platform for global investors.
We invite you to join us on this transformative journey—redefining asset management and investment through blockchain technology. Together, let’s build an equitable, transparent, and prosperous financial future.
Appendix
Glossary of Blockchain and Financial Terms
- Blockchain: A decentralized and distributed digital ledger technology that records transactions across many computers in a secure and tamper-resistant manner.
- Smart Contract: A self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, facilitating, verifying, or enforcing the negotiation or performance of an agreement.
- Tokenomics: The study and design of the economic models within a blockchain system, focusing on the creation, distribution, and utility of tokens.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): A financial system that operates on blockchain technology, offering services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
- USDC (USD Coin): A stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, used as a digital equivalent for transactions and earnings on blockchain platforms.
- Asset Token: A digital representation of ownership or interest in a real-world asset, such as real estate, solar energy projects, or tax lien investments.
- Vesting Period: A specified timeframe during which tokens allocated to team members or investors are locked and gradually released to prevent market flooding.
- DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization): A blockchain-based governance model allowing token holders to vote on decisions collectively.
- Validators: Validators are a specialized group within the LEA blockchain ecosystem responsible for ensuring the integrity and credibility of projects before they are accepted into the ecosystem.
Legal Disclaimers
- Investment Risk Acknowledgment: Participation in LEA and its associated tokens carries inherent financial risks, including the potential loss of invested principal. Prospective participants must perform comprehensive due diligence and should seek independent advice from qualified financial advisors prior to any investment.
- Non-Solicitation Notice: This document and associated materials do not constitute a solicitation, recommendation, or endorsement to buy, sell, or hold cryptocurrencies or tokens. Participation in LEA is strictly voluntary and undertaken entirely at the participant’s own discretion and responsibility.
- Regulatory Compliance: While LEA aims to adhere fully to applicable regulatory frameworks, participants bear sole responsibility for ensuring compliance with local laws, regulations, and restrictions relevant to cryptocurrency and digital asset investments within their jurisdiction.
- Platform Usage Disclaimer: The LEA platform is offered on an “as is” basis, without warranties or guarantees of any kind, explicit or implied. Users bear full responsibility for the security of their accounts and must understand and accept the operational and technological risks inherent in blockchain-based platforms.
- Forward-Looking Statements: Statements in this documentation regarding future events, expectations, projections, or anticipated outcomes are forward-looking in nature and subject to numerous uncertainties and variables. Actual outcomes or developments may differ materially from expectations or forecasts contained herein.
- Token Vesting and Distribution Transparency: Tokens allocated to the LEA team, founders, investors, and strategic partners are subject to clearly defined vesting schedules to mitigate market volatility and ensure long-term alignment with project objectives. Participants acknowledge that gradual token unlock schedules are designed to support market stability and ecosystem sustainability.
- Token Utility Clarification: Participants understand that LEA’s tokens ($LEA) are designed primarily for governance participation, transaction fee payments, staking incentives, and funding real-world asset (RWA) projects. Token value, utility, and liquidity may fluctuate significantly based on market demand, platform adoption, and regulatory developments.
